
Part 2. GRAMMATICAL CATEGORY
Date: 2015-10-07; view: 402.
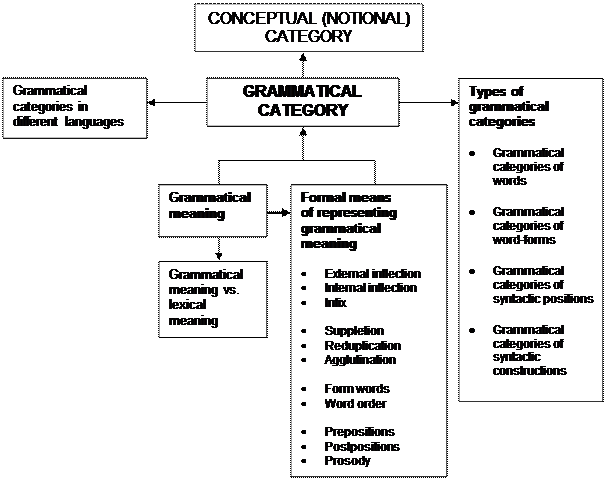 |
 |
· Define:
Grammatical category.
· Describe:
Grammatical category vs. conceptual (notional) category.
· Describe:
Grammatical meaning vs. lexical meaning.
· Innumerate:
Formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
External inflection, or ending, and its properties.
· Define:
Internal inflection as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Infix as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Suppletion as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Reduplication as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Agglutination as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Form words (grammatical words) as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Infix as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Propositions and postpositions as formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Word order as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
Prosody as a formal means of representing grammatical meaning.
· Define:
A grammeme.
Match:
- _________________ are exhibited by word classes and sub-classes. E.g. the Noun, common names, proper names, class nouns, group nouns, collective nouns, nouns of material, abstract nouns; the Adjective, qualitative adjectives, relative adjectives.
- ________________represent the types of word modifications within one and the same class, e.g. number, case, gender for nouns; degrees of comparison for adjectives.
- ________________distinguish the parts of a sentence, such as the subject and predicate, an object, attribute, and adverbial modifier.
- ________________represent the types of syntactic patterns, e.g. a phrase with coordination, a phrase with subordination, nominal phrase, verbal phrase, prepositional phrase, etc.; simple sentence, compound sentence, complex sentence, compound-complex sentence; principal clause, subordinate clause, subject clause, predicative clause, object clause, attributive clause, adverbial clause.
a) Grammatical categories of syntactic constructions.
b) Grammatical categories of word forms.
c) Grammatical categories of syntactic positions.
d) Grammatical categories of words
· Describe:
Complete and incomplete representation of grammatical categories of word forms.
· Describe:
Differences in grammatical categories of different languages (the two major cases).
| <== previous lecture | | | next lecture ==> |
| Part 1. TYPES OF GRAMMARS | | | Types of morphemes. |