
Part 3.2. DERIVATIONAL MORPHOLOGY (word-formation)
Date: 2015-10-07; view: 424.
A) Simplification (Russ. опрощение). b) Analogy. c) Grammaticalization. d) Redistribution (Russ. переразложение).
Morphological processes.
· Match:
- _____________________is a shift of boundaries between morphemes. E.g. Russ. ходи-мъ > ход-им; Old Slavic жена – жена-мъ, жена-ми, жена-хъ > Russian жен-а, жен-ами, жен-ах.
- ____________________ is a convergence of two morphemes into one, so that the number of morphemes in a word is reduced. E.g. Russ. кол-ес-о /root + suffix + inflection/ > колес-о /root + inflection/.
- ____________________ is a change of the morphological structure under the influence of similar word forms. E.g. Russ. диалектальный > диалектный (analogous to объектный, предметный, портретный); Old Russian, plural, masculine с рабы, с товарищи > с рабами с товарищами (analogous to plural, feminine с женами).
- _____________________is such a process when the lexical meaning of a word changes into the grammatical meaning. Thus, a notional word turns into an affix or a form word. E.g. Old Russian ходи + мъ, ходи + те /verb + pronoun/ > ходи-мъ, ходи-те; Russ. благо даря > благодаря /preposition/; Engl. one > an/a (an apple), this > the (the apple), to have (have asked), to be (is asking).
 |
· Define:
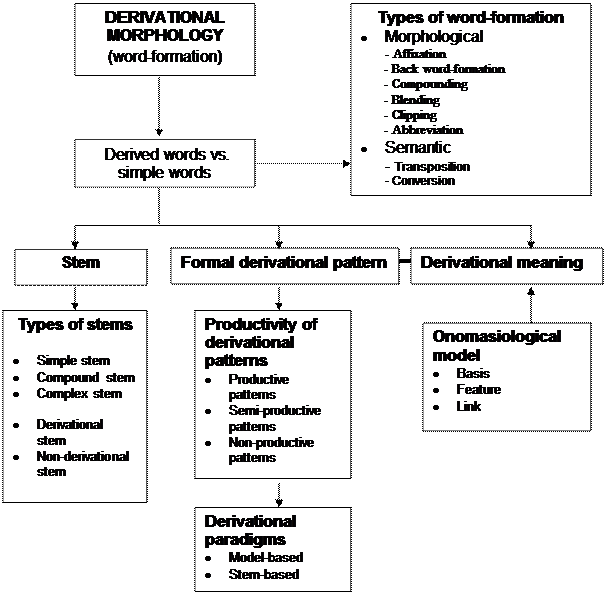
Derivational morphology vs. morphemics.
· Define:
Stem. Types of stems.
· Define:
A formal derivational pattern.
· Define:
Derivational meaning. An onomasiological model.
· Define:
Productive, semi-productive, and non-productive derivational patterns.
· Define:
Model-based and stem-based derivational paradigms.
· Define:
Affixation vs. back word-formation.
· Define:
Compounding vs. blending.
· Define:
Clipping vs. abbreviation.
· Define:
Conversion vs. transposition. Types of transposition.
| <== previous lecture | | | next lecture ==> |
| Types of morphemes. | | | Part 3.3. PARTS-OF-SPEECH THEORY |