
ACTIVE VOCABULARY
Date: 2015-10-07; view: 1308.
53.
52.
51.
50.
49.
48.
Normal Distribution (Finding observed values)
47.
46.
45.
44.
43.
42.
41.
Normal Distribution (Finding Probabilities)
40.
Poisson Approx. to Binomial
39.
37.
36.
35.
34.
33.
32.
Poisson Distribution
31.
30.
29.
Binomial Distribution
28.
27.
26.
25.
24.
23.
22.
Discrete random variables
20.
19.
18.
17.
Histograms
16.
15.
14.
Box Plots
13.
12.
11.
Statistical diagrams
10.
Quartiles
8.
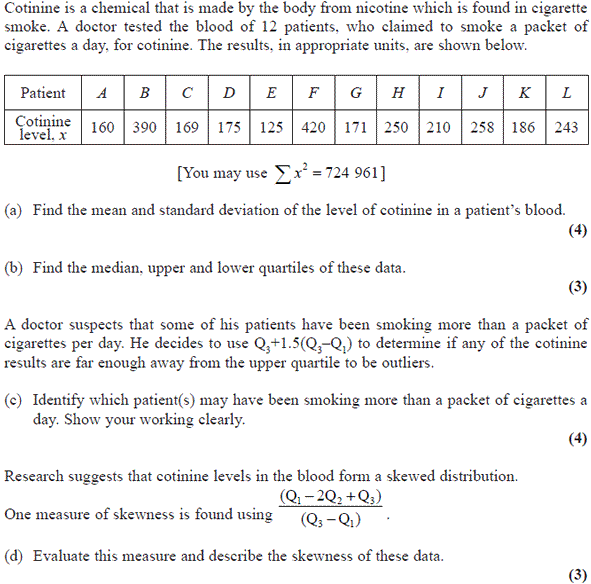
9.
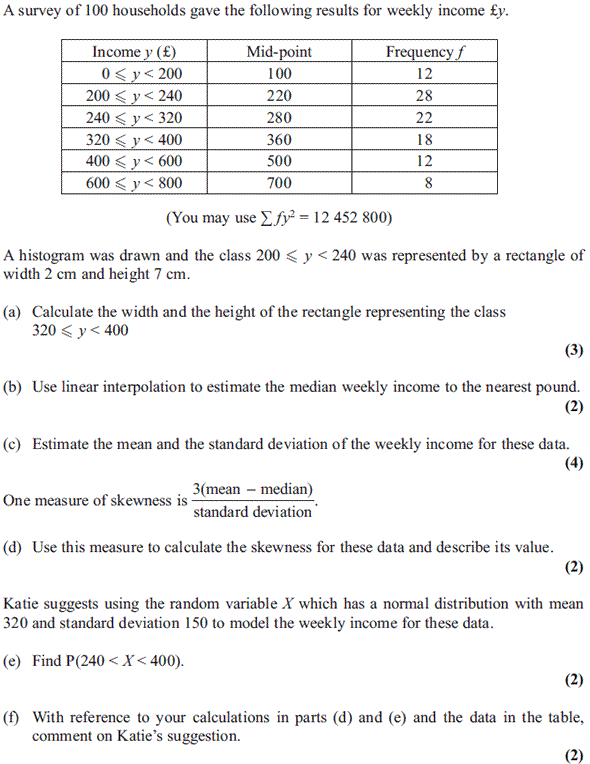
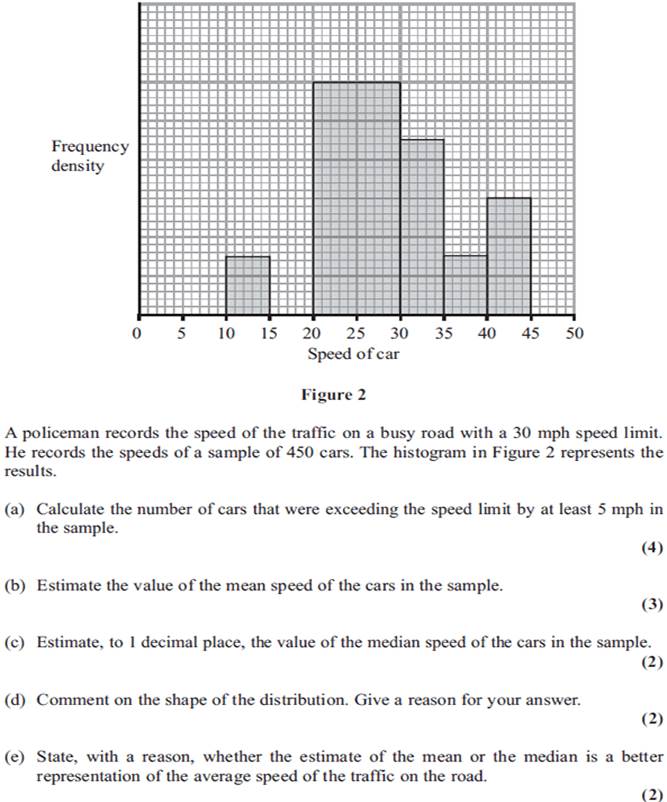



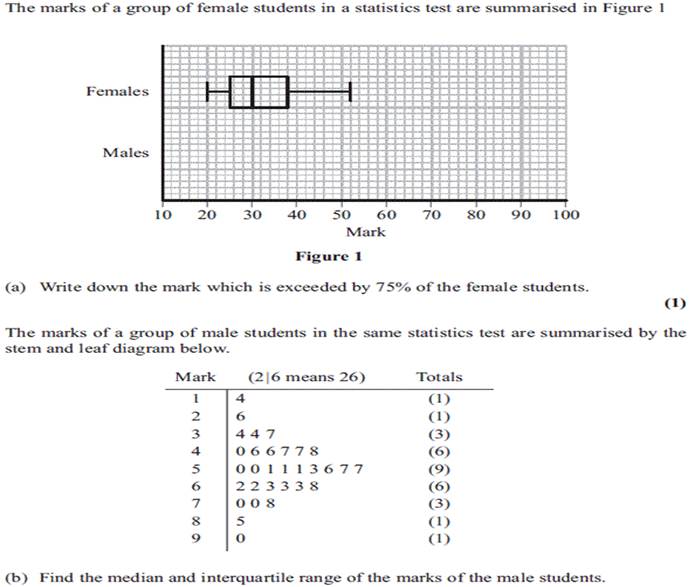



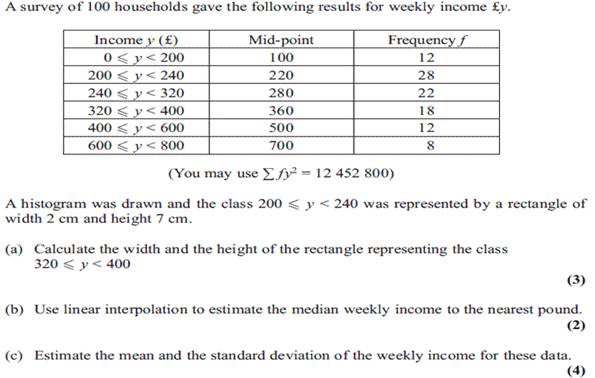
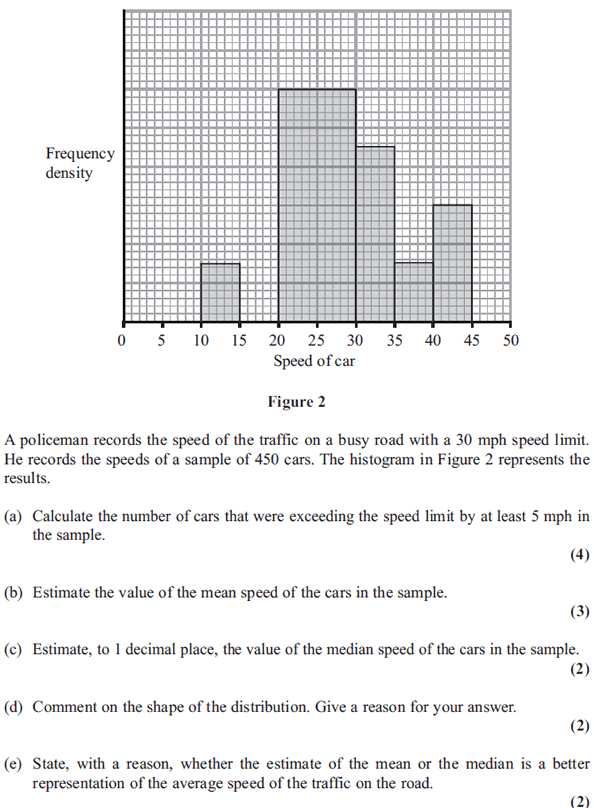
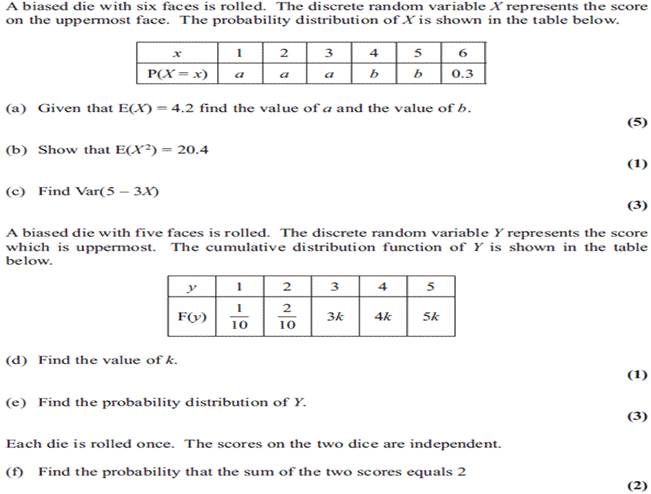
21. 



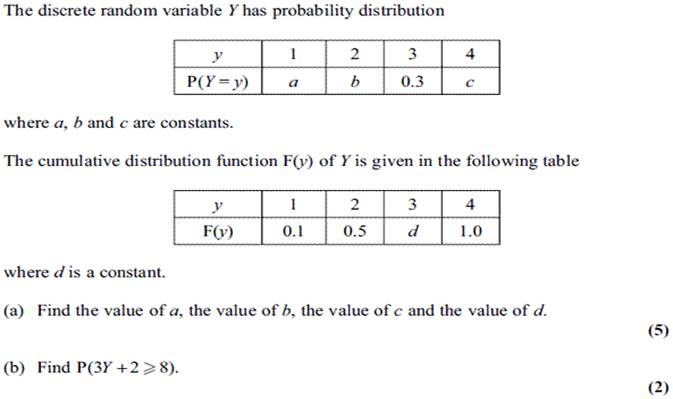
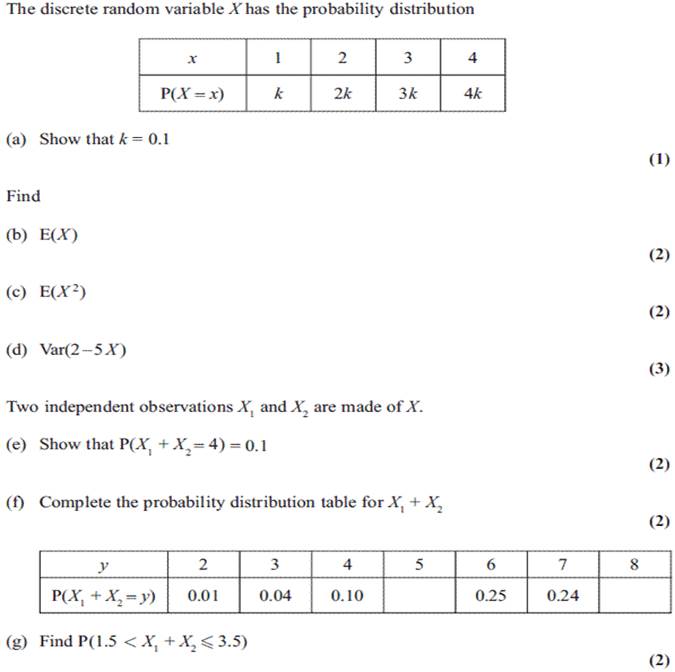











38. 











Normal Distribution (Finding Mean & Standard deviation)




assistant chefЧпомощник шеф-повара
beverageЧ напиток
busboyЧ помощник официанта, убирающий гр€зную по≠суду со стола и т. п.
captainЧ метрдотель
cashierЧ кассир г
chefЧшеф-повар
concession basisЧ на основании концессии
concessionaireЧ концессионер
dishwasherЧ посудомойка
electrical appliancesЧ электроустройства
establishmentЧ зд. штат
fixed rentЧ фиксированна€ оплата
foodЧ продукты питани€, продовольствие, съестные при≠пасы
hostessЧ зд. сотрудница ресторана или кафе, встречающа€ и усаживающа€ гостей
incomeЧ доход
kitchen helperЧ помощник на кухне
kitchen suppliersЧ поставщики
maitre d'hotelЧ метрдотель
percentageЧ процентное соотношение
premisesЧ недвижимость, здание
sommelierЧ старший официант, заведующий винами
spiritsЧ спиртные напитки
storekeeperЧ кладовщик
to be leasedЧ сданный в аренду (внаем)
waiter Чофициант
waitress Чофициантка
wines Чвина
bar Чбар, барна€ стойка
bartender Чбарменcocktail loungeЧ коктейльный зал
counterЧ стойка
fast foodЧ блюда, несложные в приготовлении
pantryЧ буфетна€, кладова€
personnelЧ штат
snack-bar (BrE), Snack bar (AmE)Ч закусочна€
soft drinksЧ безалкогольные напитки
space for storageЧ место дл€ хранени€
to cut down onЧ сокращать, снижать
to fill out a slipЧ заполнить бланк (карточку)
to simplifyЧ упрощать
to speed upЧ ускор€ть
billЧ счет
bottled(or draught) beerЧ бутылочное (или бочковое) пиво
brandЧ марка, клеймо, сорт
brewЧ варить пиво
dressing(French) Ч приправа, заправка (с растительным
маслом) main courseЧ основное блюдо snackЧ закуска to recommendЧ рекомендовать
Special terms:
Maitre d'Ч a person in charge of a restaurant who tells guests where to sit and waiters what to do, etc.
ChefЧa skilled, usually male cook, especially the chef cook in a hotel or restaurant.
StewardЧ a restaurant employee who serves wines and some≠times other drinks. The person is called the sommelier in French, an expression also is used in English.
WaiterЧ an employee in a restaurant who goes to the custom≠ers' tables, takes their orders and then brings the prepared food to the tables.
Room ServiceЧ the supplying, on demand, of food and bever≠age service to the guest rooms of a hotel.
ConcessionЧ a form of licence, granted for a fee by the hotel owner to an outside company, to conduct business on the hotel premises. For example, a company that contracts to operate the hotel's restaurants is said to have the food concession. The person or firm that performs the service is the concessionaire.
CaptainЧ the employee who seats a guest in a restaurant.
TEXT 1 ■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
FOOD AND BEVERAGE DEPARTMENT (PART 1)-RESTAURANTS
Every modern hotel offers some form of food and beverage service. In some, facilities are available only for a continental breakfast Ч that is, a light meal of bread or rolls and coffee Ч. while others have a small coffee shop or restaurant on the pre- mises. In many small hotels or motels, these food services are operated on a concession basis: the facility is leased to an outside operator, called the concessionaire, who pays the own≠ers of the hotel either a fixed rent or a percentage qf the income. Many other hotels have complete restaurant service and also of≠fer room service for guests who desire food and beverages served to them in their rooms. Large hotels, including the more luxu≠rious resort hotels, usually offer a great variety of restaurants and bars for their guests to choose from. The restaurants may have different price ranges and/or different menus.
Food and beverage service is a major factor in hotel opera≠tion. In some large hotels, the income derived from this source actually exceeds income from room rentals. The food and bev≠erage income in many hotels is increased by providing service for banquets and conventions.
Because of the large proportion of income contributed by a hotel's bars and restaurants, the food and beverage manager is a key member of the management staff. He has the overall re≠sponsibility for planning the food and drink operation pur- chasing the hundreds of items that are necessary for the restau≠rants and bars. Because food can spoil quickly, ordering supplies is a daily activity. In a very large establishment, two people may be assigned to this task Ч one to order food and the other to order wines and spirits. The food and beverage manager's staff may also include a storekeeper, who stores and issues food, bev≠erages and restaurant and kitchen supplies.
The kitchen itself is almost a separate kingdom within the hotel. The head cook, almost always designated by the French word Chef, is the boss. The chef is responsible for planning the menus Ч- that is, the food ffiat is being served on a particular day Ч and for supervising the work of the other chefs and cooks.
Depending on the size of the establishment, several assistant chefs report to the chef. These include a sauce chef a salad chef a vegetable chefmd so on. Under the supervision of the chefs are the cooks who actually place it on the plate for the waiters to pick up. Under the cook's supervi≠sion are the kitchen helpers who, for example, peel potatoes, cutup vegetables, and bring food from the storeroom to the kitch≠en. The kitchen staff also includes dishwashes, even in a kitch≠en equipped with electrical appliances, since pots and pans usu≠ally need special attention, and someone must load and unload the machines.
In the restaurant, as well as in the kitchen, there are also dif≠ferent kinds of jobs. The person who seats the guests is called captain or maitre d' (short for maitre df hotel, another French ex≠pression that keeps appearing in the hotel and restaurant busi≠ness), or a hostess, if a woman. In restaurants with a very for≠mal style of service, the captain also takes the guests' orders. The meals are served by waiters or waitresses. In less formal restau≠rants, the waiters and waitresses take orders and serve the meals. Most restaurants also employ busboys, who pour water, clear and set tables, and perform other similar chores. In some restaurants, however, the waiters and waitresses carry out these tasks. In an elaborate restaurant, there is often an employee called the wine steward or sommelier, who takes orders for wine and sometimes for other alcoholic drinks. Finally, there are cashiers who receive payment or signed bills from the guests. When the guest puts his restaurant bill on his hotel account, this information must be passed along to the accounting office as quickly as possible.
(by E.J. Hall)
Comprehension questions:
1.What kinds of food and beverage service are offered by hotels?
2. Why is food and beverage service a major factor in hotel operations?
3. Why is the food and beverage manager a key member of the management staff? What is his overall responsibility?
4. What employees may work on the food and beverage manager's staff?
5. Who is the head of the kitchen staff? What is he respon≠sible for?
6. What does the job of an assistant chef consist of?
7. Who are some of the other employees in the kitchen?
8. What are the duties of the captain in a restaurant?
9. What are the duties of the waiters and waitresses? What may they do in restaurants that do not have a formal style of service?
10. Who performs chores such as clearing and setting tables?
11. Who takes orders for wine and other drinks in some res≠taurants?
12. What do the cashiers in the restaurant do?
TEXT WORK ■ ■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1. Phonetic Drill. Transcribe and pronounce correctly:
Concession, leased, concessionaire, percentage, exceed, contribute, supplier, assigned, chef, supervise, maitre d'hotel, steward, sommelier, cashier.
2. Find English equivalents in the text:
(1) посто€нна€ оплата (2) процент с дохода (3) обслужи≠вание в номере (4) различные цены (5) основной фактор в управлении отел€ми (6) получаемый доход (7) превышать доход (8) доход увеличиваетс€ за счет обслуживани€ банке≠тов и конференций (9) основной член управл€ющего со≠става (10) ответственность за планирование (11) заказ по≠ставок (12) вина и спиртные напитки (13) шеф-повар ответственен за составление меню (14) контролировать работу (15) под руководством (16) оборудованна€ электри≠ческими приборами (17) загружать и разгружать (18) при≠нимать заказы (19) принимать оплату (20) включать-счет ресторана в счет оплаты за отель
3. Explain parts in italics and reproduce the situations in
which sentences occur in the text:
1) In many small hotels or motels food services are often
2) The restaurants may have different price ranges and dif≠ferent menus.
3) In some large hotels, the income derived from this source actually exceeds income from room rentals.
4) The food and beverage manager is a key member of the management staff
5) In a very large establishment, two people may be assigned to this task Ч one to order food and the other to order wines and spirits.
6) The kitchen staff also includes dishwashes, even in a kitch≠en equipped with electrical appliances.
7) When the guest puts his restaurant bill on his hotel ac≠count, this information must be passed along to the ac≠counting office as quickly as possible.
4. Reproduce the sentences in which the following words
and expressions are used:
1) is leased to an outside operator
2) a great variety of restaurants and bars
3) income is increased
4) under of supervision of the chefs
5) someone must load and unload the machines
5. Fill in the blanks with prepositions and adverbs:
(1) Large hotels, including the more luxurious resort hotels, usually offer a great variety ... restaurants and bars ... their guests to choose .... (2) Because Е the large proportionЕ income con≠tributed Е a hotel's bars and restaurants, the food and bever≠age manager is a key member Е the management staff. (3) The chef is responsibleЕ planning the menus Ч that is, the food that is being served Е a particular day Ч and supervising the work ftp the other chefs and cooks. (4) Depending ..: the size ... the establishment, several assistant chefs reportЕ the chef. (5) ... the supervision ... the chefs are the cooks who actually cook the food and then place it Е the plate Е the waiters to pick Е . (6) When the guest puts his restaurant bill Еhis hotel account, this information must be passed the accounting officeЕquickly Еpossible. (7) The food and beverage income Е many hotels is increased Е.. providing service Е. banquets and conven≠tions.
.
6. Draw a chart like the one below and arrange restaurant jobs into two columns:
| Management staff | Unskilled employees |
Compare your chart with the rest of the group and discuss it using the following words: interesting, creative, boring, relaxing, terrible, difficult, tiresome... etc.
7. Write the derivatives to the following words in the box:
Owner To operate Responsibility
Establishment Supervision To supply
8. Explain the meaningof the following terms and use
them in the sentencesof your own:
Chef, sommelier, waiter, busboy, maitre d'hotel.
| <== previous lecture | | | next lecture ==> |
| IDIOMATIC EXPRESSIONS | | | AND ROOM SERVICE |