
III. Scottish English
Date: 2015-10-07; view: 553.
We must first make clear that the status of Scottish English is still debated. Some linguists say that it is a national variant. Others say that it is a dialect.
English has been spoken in Scotland for as long as it has been spoken in England. In the Highlands and Islands of north-em and western Scotland, however, Gaelic is still the native lan
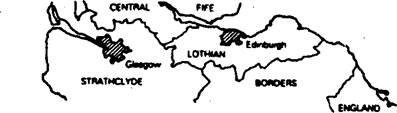
guage of thousands of speakers from these regions. A standardized form of this language, known as Scots, was used at the court and in literature until the Reformation. Then it was gradually replaced by English. Incidentally a number of writers and poets of the likes of R. Bums retained their native language.
Nowadays educated Scottish people speak a form of Scottish Standard English which grammatically and lexically is not different from English used elsewhere, although with an obvious Scottish accent. We must admit, however, that non-standard dialects of Scotland still resemble Scots and in many respects are radically different from most other varieties of English. It is very difficult to understand them for students who learn RP.
At the moment there is currently a strong movement in Scotland for the revival of Scots. Nevertheless Scottish Standard English is still more prestigeous and in this book we concentrate on Scottish English as used and spoken by educated urban Scots.
As for the status of Scottish English, in this book it will be treated as a dialect though it is fair to say that there is much in favour of calling it a national variant of English.
Vowels
1. Since Sc. Eng. is rhotic, i.e. it preserves post-vocalic [r], vowels such as RP [iə], [ɜ:], [ɛə], [uə] do not occur:
| RP | Sc. Eng. | |
| beer | [biə] | [bir] |
| bird | [bɜ:d] | [bird] |
| hurt | [hɜ:t] | [hʌrt] |
| bard | [ba:d] | [ba:rd] |
| moor | [muə] | [mur] |
2. Length is not a distinctive feature of Scottish vowels. So pairs like pool — pull, cot — caught are not distinguished. It should be noted, however, that vowels are longer in final stressed open syllables than elsewhere.
3. Monophthongs are pure, there is no trace of diphthongiza-tion with the exceptions of [ai — ɛi], [au — ɛu] and [ɔı].
4. The RP [æ — ɑ:(a)] distinction doesn't exist: hat [hat], dance [da:ns],
5. [i], [u], [ʌ], [ə] may be central.
6. In non-standard Sc. Eng. accent [u:] often occurs when RP has [au]: house [haus — hu:s]
7. It is interesting to mention that [ɒ] and [ɜu] may be not contrasted:
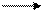 socks [soks]
socks [soks]
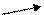 soaks
soaks
 not [not]
not [not]
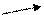 note
note
8. In very many regional accents do, to are pronounced as [de], [tə].
9. In some accents words such as arm, after, grass may have [ɛ] rather than [a:]: after ['ɛftə].
Consonants
1. Sc. Eng. consistently preserves a distinction between [ʍ] and [w]: which [ʍiʧ] — witch [wiʧ].
2. Initial [p, t, k] are usually non-aspirated.
3. [r] is most usually a flap.
4. Non-initial [t] is often realized as glottal stop [ʔ].
5. [ł] is dark in all positions.
6. The velar fricative [x] occurs in a number of words: loch [lɒx].
7. -ing is [in].
8. [h] is present.
9. A specific Scottish feature is the pronunciation of [Ɵr] as [ʃr]: through [ʃru:].
| <== previous lecture | | | next lecture ==> |
| II. Welsh English | | | IV. Northern Ireland English |