
Gene diseases (molecular diseases).
Date: 2015-10-07; view: 512.
Plural congenital disorders of ontogenesis are the results of gene mutation. The mechanism of these diseases' (syndromes)genesis is the mechanism of primary pleiotropy. At present several thousand of such syndromes are known. Marfan's syndrome is a classical example. The syndrome includes some characters: aneurysm of aorta, hypermobility of joints, and arachnodactilia (long, very good mobility fingers).
Diseases of metabolism disorders. The causes of these diseases are mutations of genes coding ferments, transport proteins, or structural proteins. Genesis of the diseases occurs according the mechanism of secondary pleiotropy. In the case of mutation of a gene coding ferment, the ferment's activity or quantity, or the ferment's quality is changed. And normal biochemical reaction becomes more slowly, or the reaction stops. Quantities of some substances get increase, and some substances get decrease. It named fermentopatia.
Categorization of metabolism diseases
1. Disorders of protein metabolism.
2. Disorders of amino acids metabolism.
3. Disorders of lipids metabolism.
4. Disorders of carbohydrates metabolism.
5. Disorders of metabolism of mineral materials.
Thalassemia and sickle cells anemia are the examples of protein metabolism disorders. There is a mutation of gene coding a protein of hemoglobin (figure 31.8). As a result the shape of erythrocytes is changed, and they destruct very easy. And the anemia occurs.
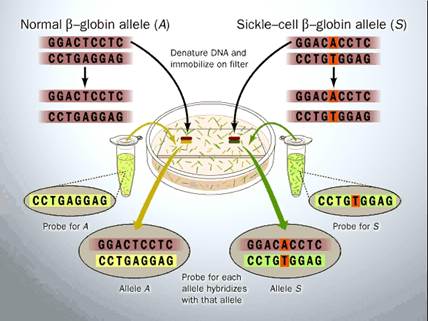
Figure 31.8. Mutation of gene coding protein of hemoglobin
Phenylketonuria and albinism are typical disorders of amino acids metabolism.
At the albinism in consequence of gene mutations a ferment thyrosinase suffers. So the current reaction of tyrosine metabolizing to melanin is broken. And quantity of melamine is getting less. As a result the color of skin become white, and iris of eye become red.
The cause of pathogenesis of phenylketonuria is the mutation of ferment phenylalaninehydroxylase's gene. The metabolizing of phenylalanine to tyrosine is blocked (figure 31.9). The abnormal pathway of phenylalanine arises. As a result the accumulation of phenylketones take place. Phenylketones are tocsins for nervous system, thus the lag of mental development, severe mental retardation and some other symptoms arises (figure 31.10).
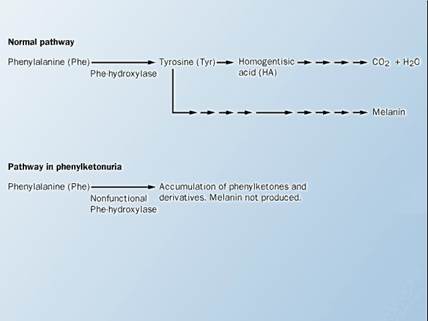
Figure 31.9 Block of phenylalanine normal metabolism

Figure 31.10 Phenylketonuria is autosomal recessive defect of metabolism
The example of lipids metabolism disorder is infantile type of cerebral sphingolipidosis (gangliosidosis or Tay-Sachs disease). Some data from description of the disease are at the figure 31.11. Tay-Sachs Disease is an autosomal recessive resulting in degeneration of the nervous system. Symptoms manifest after birth. Children homozygous recessive for this allele rarely survive past five years of age. Sufferers lack the ability to make the enzyme N-acetyl-hexosaminidase, which breaks down the GM2 ganglioside lipid. This lipid accumulates in lysosomes in brain cells, eventually killing the brain cells. Although rare in the general population (1 in 300,000 births), it was (until recently) higher (1 in 3600 births) among Jews of eastern central European descent. One in 28 American Jews is thought to be a carrier, since 90% of the American Jewish population emigrated from those areas in Europe. Most Tay-Sachs babies born in the US are born to non-Jewish parents, who did not undergo testing programs that most US Jewish prospective parents had.

Figure 31.11. Tay-Sachs disease (a lysosomal disease resulting from hexominidase deficiency
Galactosemia is an example of carbohydrates metabolism disorder. The cause of pathogenesis of phenylketonuria is the mutation of gene that includes information about the ferment named galactose-1-phosphaturidiletransferase.
Podagra and Wilson's disease are examples of disorder of metabolism of minerals. The mutation of gene of a transport protein is the basis of pathogenesis of Wilson's disease. The transport of copper is the function of the protein. As a result the excess of cooper come into cerebrum and liver and morphological changes and functional disorders of these organs are arisen.
| <== previous lecture | | | next lecture ==> |
| Chromosome diseases. | | | Methods of prevention of the hereditary diseases. |