
Unit 12 THE GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE
Date: 2015-10-07; view: 582.
Explore
Useful Language
He/She needs/wants _____ (features) because _____ (reason).

With this software, he/she can/will be able to _____ (benefits).
· in groups:
What software do you use in your university/home? Why do you use it? What can you do with this software?
· with a partner:
Choose one kind of software and list its features and benefits. Then tell the class.
Exercise 1.The picture below illustrates a user interface based on graphics.
Read the definitions in the HELP box and then find the following interface elements in the picture:
1 window 7 disk icons
2 scroll bars 8 folders
3 menu bar 9 program icons
4 pull-down menu 10 document icons
5 pointer 11 printer icon
6 toolbar buttons 12 dock icons
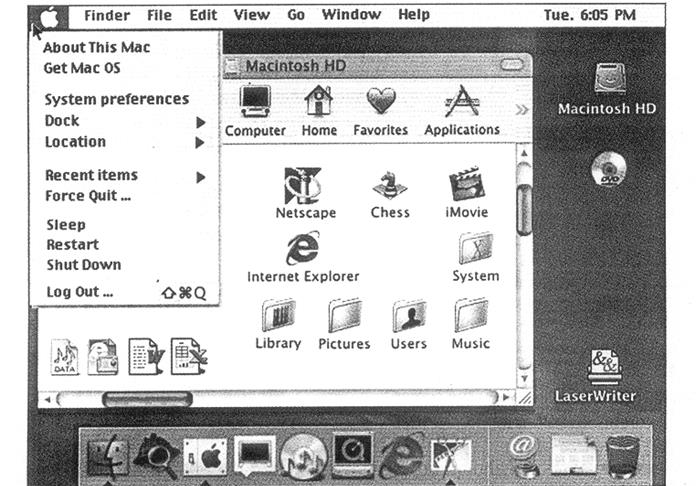
| HELP box |
| · window: à viewing area less than or equal to the screen size. By using different windows you can work on several documents or applications simultaneously · pull-down menu: à menu that the user 'pulls down' from à name in the menu bar at the top of the screen by selecting the name with the mouse · the pointer:an arrow, controlled by the mouse, that allows you to move around the screen · toolbar buttons: found at the top of à window, they take you to the Íîòå folder and others · icons: graphic images (or intuitive symbols) used to represent an object or task · folders: containers for documents and applications · dock: set of icons at the bottom of the screen that give you instant access to the things you use most |
Exercise 2.Read the article below and decide which of the expressions in the box best describe à graphical user interface (GUI).
| user-friendly slow attractive text-based complex graphics-based |
GUIs
The term user interfacerefers to the standard procedures the user follows to interact with à particular computer. À few years ago, the way in which users had access to à computer system was quite complex. They had to memorize and type à lot of commands just to see the content of à disk, to copy files or to respond to à single prompt. In fact, only experts used computers, so there was no need for à user-friendly interface. Now, however, computers are used by all kinds of people and as à result there is à growing emphasis on the user interface.
À good user interface is important because when you buy à program you want to use it easily. Moreover, à graphical user interface saves à lot of time: you don't need to memorize commands in order to execute an application; you only have to point and click so that its content appears on the screen.
Macintosh computers — with à user interface based on graphics and intuitive tools — were designed with à single dear aim: to facilitate interaction with the computer. This interface is called WIMP: Window, Icon, Menu (or Mouse)and Pointerand software products for the Macintosh have been designed to take full advantage of its features using this interface. In addition, the ROM chips of à Macintosh contain libraries that provide program developers with routines for generating windows, dialogue boxes, icons and ðîð-up menus. This ensures the creation of applications with à high level of consistency.
Today, the most innovative GUIs are the Macintosh, Microsoft Windows and IBM ÎS/2 Warp. These three platforms include similar features: à desktop with icons, windows and folders, à printer selector, à file finder, à control panel and various desk accessories. Double-clicking à folder opens à window which contains programs, documents or further nested folders. At any time within à folder, you can launch the desired program or document by double-clicking the icon, or you can drag it to another location.
The three platforms differ in other areas such as device installation, network connectivity or compatibility with application programs.
These interfaces have been so successful because they are extremely easy to use. It is well known that computers running under an attractive interface stimulate users to be more creative and produce high quality results, which has à major impact on the general public.
Exercise 3.Look at the text again and guess the meaning of these words in your own language.
| <== previous lecture | | | next lecture ==> |
| Exercise 4. Language work | | | Program developer nested folders |