
Определители второго и третьего порядка и их вычисление. Определение определителя любого порядка. Алгебраические дополнения. Перечислить свойства определителя.
Date: 2015-10-07; view: 592.
1/2
B(-13, -17)
164. Find the length of the minor axis of the ellipse with center (0,0), foci (0,±3) and vertex (0,5).
b= 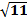
165. Find equation of a circle which center C(2,-3) and radius is R=6.

166. Let A (4,6) , B (4,0) , C (1,4) be vertices of the triangle. Find the equation of side AB.
6x-8y+24=0
167. Let A (4,6) , B (4,0) , C (1,4) be vertices of the triangle. Find the equation of side BC.
3y+4y+16=0
168. Let A (4,6) , B (4,0) , C (1,4) be vertices of the triangle. Find the equation of the height
from vertex A .
4y-3y+2=0
169. Let A (4,6) , B (4,0) , C (1,4) be vertices of the triangle. Find equation of the median
dropped from vertex C.
y-7y-3=0
170. Find equation of the straight line through the point A(-1,-3) if the angle between it and the
Y-axis is 450.
171. Find equation of the straight line through the point A(-1,-3) if the angle between it and the эти три примера лучше перерешать)))
Y-axis is 300.
172. Find equation of the straight line through the point A(-1,-3) if the angle between it and the
Y-axis is 1800.
173. Two points A(3,1), B(3,7) are given. Find coordinates of point M on Y-axis such that
straight lines AM and BM are mutually perpendicular.
Y=22
174. Find distance from the origin to the straight line: 9x 12y 10 0.
D=2/3
175. Find angle between straight lines 2x y 5 0 and 6x 2y 7 0 .
45 
176. Find distance from the origin to the straight line x-y=0.
D=0
177. Determine a so that the lines 3ax 8y 13 0 and (a 1)x 2ay 21 0 are parallel.
a1=2; a2= -2/3
178. Find the equation of the straight line through the point P(5,2) and perpendicular to the
straight line 4x y 3 0 .
x+4y+18=0
179. Find equation of the plane that passed through the point (2,5,3) and is parallel to the
coordinate plane XOZ.
x+z-5=0
180. Find equation of the plane through the three points M1(1, 2, -1); M2(-1, 0 , 4); M3(-2, -1, 1).
11x-11y+12z+23=0
181. Find equation of the plane through point A(1,2-4) and is parallel to the XOY-plane.
X+y-3=0
182. Find distance between two parallel planes: 5x + 3y - 4z + 15 = 0; 15x + 9y - 12z - 5 = 0.
D=- 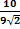
183. Find distance between two parallel planes: 11x 2y 10z 15 0, 11x 2y 10z 45 0.
D=-4
184. Find the volume of the tetrahedron if its vertices are A(0,0,2), B(3,0,5), C(1,1,0), D(4,1,2) .
185. Coordinates of vertices of triangle ABC are A(1,6), B(-5,4), C(2,-3). Find angle at vertex B.
Arccos( 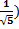
186. Find angle between the line 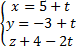 and the plane 4x-2y-2z+7=0.
and the plane 4x-2y-2z+7=0.
60 
187. Find the angle between the planes 3y-z=0 and 2y-z=0.
Arccos( 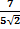 )
)
188. Find canonical equation of the line x y z 2 0, x 2y z 4 0.
189. Find equation of the line through point M(5,-2) and parallel to the OY-axis.
X=5
190. In the triangle ABC find length of the altitude (height) AH if: A(1,-8), B(7,2), C(-5,2)
191. Find equation of the plane through the point (2,-1,5) and parallel to the plane x-3y+5z-1=0.
x-3y+5z-24=0
192. Find equation of the plane passing through the point (2,5,3) and is parallel to the coordinate
plane XOY.
X+Y-7=0
193. Find point of intersection of straight line 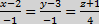 and plane x 2y 3z 14 0.
and plane x 2y 3z 14 0.
M(1,2,3)
194. Find area of the parallelogram formed by vectors a and b: a p 2q , b 3p q; Тупо не знаем как решать XD
p 1, q 2, ( p^ q) / 6.
195. Find area of the parallelogram formed by vectors a and b: a 3p q , b p 2q;
p 4, q 1, ( p^ q) / 4.
196. Find area of the parallelogram formed by vectors a and b: a 10p q , b 3p 2q;
p 4, q 1, ( p^ q) / 6.
-46 ß вроде как))))
197. Find canonical equation of the line passing through point M(1,0,-2) and parallel to the vector
s 2i 3 j .
2x-3y-1=0 and Not my answer: x=1
198. Find angle between straight lines 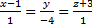 And
And 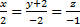
45 
199. Find the values of α and β such that vector a (3,1,) is perpendicular to the vector
b (2,,1) if b 3.
a=-4 and not my answer: a=-8
200. Find distance between two points A(5,2) and B(3,-3).
D= 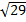
Определитель (детерминант) – число, которое ставится в соответствие квадратной таблице чисел по определенным правилам.
Определитель второго порядка: 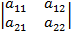 =
= 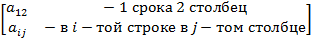 =
= 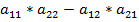
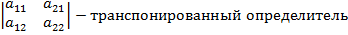
При транспонировании определитель не меняется.
Определитель = 0, когда: 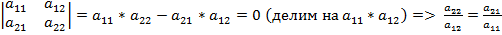
или 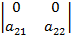 =0
=0
Определитель 3-го порядка - 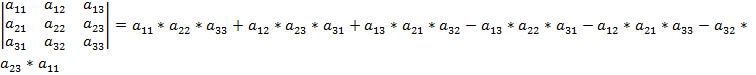
или 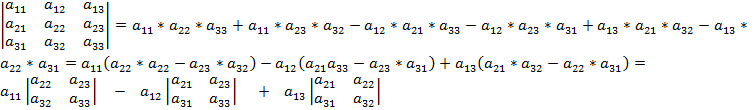
(минор 1 элемента) (минор 2 элемента) (минор 3 элемента)
Если минор домножить на «-», то он становится алгебраическим дополнением.
Aij=Mij*(-1)i+j
Определитель n-ого порядка: 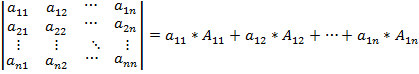
Свойства:
1) При транспонировании определитель не меняется.
2) При перестановке любых 2 строк(столбцов) определитель меняет знак.
3) Если в определителе 2 строки (столбца) одинаковы, то определитель = 0.
4) Если какая либо строка или столбец состоит только из 0, то определитель = 0.
5) Если в определителе 2 строки или 2 столбца пропорциональны, то определитель = 0.
6) Число, умноженное на определитель = определителю у которого одна строка или столбец умножена на это число.
7) Пусть 2 определителя отличаются только 2 строками, тогда сумма определителя = определителю, у которого одинаковые строки остаются, а не одинаковые складываются.
Пример: 
8) Если какая то строка является линейной комбинацией остальных строк, то определитель = 0.
9) Если в какой-либо строке добавить линейную комбинацию каких-нибудь других строк, то определитель не меняется.
10) Определитель = сумме произведений элементов какой-либо одной строки на их алгебраическое дополнение.
11) Сумма произведений элементов какой-либо строки (или какого-либо столбца) определителя на соответствующие алгебраические дополнения элементов любой другой строки (любого другого столбца) равна нулю.
12) Определитель = 0, ó какая-либо строка является линейной комбинацией другой строки.
Будем говорить, что некоторая строка (а1, a2, ..., аn) является линейной комбинацией строк (b1, b2, ...,bn), (c1 c2, ..., cn), .... (d1 d2, .... dn) с коэффициентами λ, μ, ...,ν, если аj= λbj + μcj + ... + νdj для всех j— 1, 2, .... n.
| <== previous lecture | | | next lecture ==> |
| S(-1,3,-1)//// ne dodelal | | | Определение вектора. Равенство векторов. Сумма векторов и ее свойства. Произведения векторов и числа и его свойства. |